President Donald Trump said the “big Oil Deal” he brokered will save hundreds of thousands of American jobs. But the agreement hinges on a shale bust that could spell the end for some explorers drowning in debt, bringing a wave of bankruptcies and job losses.
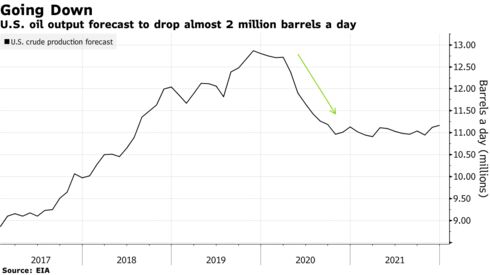
On Sunday, the OPEC+ group agreed to pare production by 9.7 million barrels a day, ending a devastating price war between Saudi Arabia and Russia. Trump, meanwhile, is counting on market forces to shave some 2 million barrels a day of overall U.S. output by the end of the year.
U.S.-focused oil producers have already slashed more than $27 billion from drilling budgets this year and are starting to shut in production. And almost 40% of oil and natural gas producers face insolvency within the year if crude prices remain near $30 a barrel, according to a survey by the Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City.
“Trump’s strategy seems to rely on the free market forcing production down and implicit in that is some companies going under,” said Dan Eberhart, a Trump donor and chief executive of drilling services company Canary Drilling Services.
Explorers idled 10% of the U.S. oil-drilling fleet, with more than half of the losses in the Permian Basin of West Texas and New Mexico, the heart of America’s shale industry, while Concho Resources Inc. said that it and other producers are shutting in output. Oil producer Whiting Petroleum Corp. and service provider Hornbeck Offshore Services Inc. headed for bankruptcy.
After the deal, Goldman Sachs Group Inc. analysts called the deal “too little, too late”, and said they expect inland U.S. crude prices to decline further in coming weeks as storage fills up. Prices fell below $10 a barrel in some areas of the U.S. during March due to the collapse in demand, with at least one grade bid at negative prices.
Oil futures in New York were up 3.2% to $23.48 a barrel Monday, but well off their initial surge following the deal.
Scott Sheffield, chief executive officer of shale driller Pioneer Natural Resources Co., said he’ll testify at a meeting of Texas regulators on Tuesday to argue for a 20% cut to the state’s oil production in May. The OPEC+ deal to lower output is “not enough” and more is needed from non-OPEC nations including the U.S. to stabilize crude prices, Sheffield said in an interview with Bloomberg Television. Texas should tie cuts to more reductions from G-20 nations, he said.
Oil giants Exxon Mobil Corp. and Chevron Corp., along with most of the other prominent Texas shale explorers, oppose mandated cuts.
Meanwhile, refiners, running out of places to store fuel they can’t sell, are cutting back production and turning away crude they don’t need, adding to pressure on smaller producers.
Scaling Back
Trump’s strategy in pressing the Saudis and Russians to agree to sweeping cuts hinged on his oft-repeated claim that U.S. drillers were already scaling back of their own accord in response to the downturn. Some senators from oil-producing states previously raised the prospect of cutting off aid to Saudi Arabia or slapping tariffs on its crude if the kingdom didn’t pare output.
Trump has pointed out that the oil could be pumped later. “Well, there’s no real cost because we’re agreeing to produce a little bit less,” he said at a press conference Friday. “It’s staying in the ground. You have it. You have it for another day.”
Two of the biggest industry trade groups, which opposed the idea of tariffs, expressed support for the deal. The American Petroleum Institute welcomed the “announcement of an agreement by other producing nations to follow the lead of the global marketplace – and U.S. producers – to reduce supply to align with lower energy demand as result of the pandemic.” The American Fuel & Petrochemical Manufacturers was pleased that a deal was reached that “helps U.S. producers and avoids imposing added costs on U.S. refiners.”
With demand destruction outstripping the pledged cuts by a long way, the agreement isn’t so much about balancing markets so much as buying time to prevent stockpiles from overflowing, said Kevin Book, managing director at ClearView Energy Partners LLC in Washington.
“The problem shale has is the same problem every producer has — the low-cost producers will win, relative to the high-cost producers but everyone right now is losing,” Book said. “So what does it mean when everyone’s losing and you’re losing less? Some U.S. producers will weather the storm better than others. I don’t think you can paint shale with a single brush.”
Read it from bloomberg – Photo as posted on Bloomberg ( Oil storage tanks stand illuminated at night at the RN-Tuapsinsky refinery in Tuapse, Russia, on March 22. Photographer: Andrey Rudakov/Bloomberg )



